
How to Share Sensitive Content Securely in Adherence to NIST 800-171
Organizations that process, share, or store controlled unclassified information (CUI) must adhere to specific standards and regulations to ensure the security and integrity of this information. One such standard is the National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication (NIST SP 800-171), which provides guidelines for protecting CUI in non-federal systems. This blog post delves into NIST 800-171 as it relates to CUI and provides best practices for secure file sharing and transfers in adherence to NIST 800-171.
NIST 800-171 Special Publication Origin and Scope
NIST 800-171 was created in response to a mandate from the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to protect sensitive government information. The guidelines outline specific security requirements for organizations that handle controlled unclassified information (CUI), which includes information that is sensitive but not classified. Compliance with NIST 800-171 is critical for protecting this sensitive content from unauthorized access and ensuring the security of government information.
The scope of NIST 800-171 extends beyond federal agencies and applies to contractors, subcontractors, and suppliers who process, store, or transmit CUI on behalf of the government. Compliance with NIST 800-171 is necessary to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of CUI.
NIST 800-171 encompasses a set of security controls and safeguards that organizations must implement to protect their information systems—including the CUI these systems hold—effectively. These controls cover various aspects, including risk assessment, incident response, access controls, and personnel security. By adhering to these controls, organizations can fortify their defenses against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Importance of Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information
Sensitive content communications, in the context of CUI, refers to the exchange of unclassified information that requires safeguarding or protection due to its sensitive nature. CUI is a category of information that is controlled and regulated by the U.S. federal government to ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Sensitive content can exist in various formats, including documents, emails, images, audio files, and video recordings.
CUI can include a wide range of information types, such as:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Information that can be used to identify individuals, such as Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, or financial records.
- Law Enforcement Sensitive (LES) Information: Information related to ongoing law enforcement activities, investigations, or intelligence operations that, if disclosed, could jeopardize these activities.
- Export-controlled Information: Information related to technologies, products, or services that are subject to export control laws and regulations due to their potential impact on national security, foreign policy, or economic interests.
- Proprietary Business Information: Information that is confidential and proprietary to a business, such as trade secrets, financial data, or client lists.
- Protected Health Information (PHI): Information related to an individual’s medical or healthcare records that is protected under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States.
Ensuring the security and privacy of this information as it’s sent, shared, received, or stored is vital to protect the privacy of individuals and organizations. Failure to safeguard such content can lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, litigation, compliance violations, financial losses, and reputational damage. Adherence to a robust framework like NIST 800-171 helps organizations protect CUI in transit and at rest from the risk of unauthorized access.
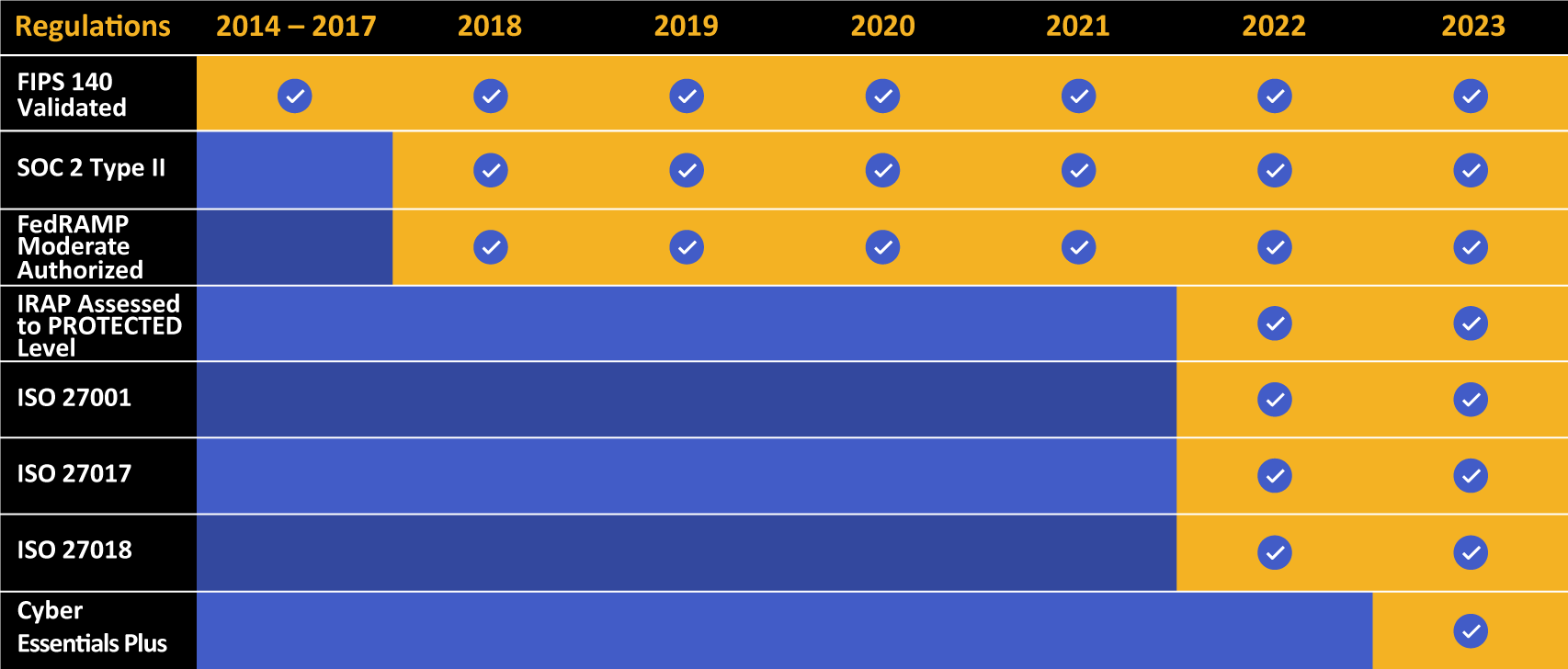
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Compliance Requirements for NIST 800-171
NIST 800-171 contains 110 security requirements, grouped into 14 security control families. These controls cover various aspects of information security, including access control, incident response, media protection, and system and communications protection. Implementing these controls helps ensure the protection of CUI in transit and at rest.
Let’s explore some of these controls in greater detail:
NIST 800-171 Security Assessment Control Family
Conducting regular security assessments allows organizations to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their systems. By performing comprehensive audits and vulnerability scans, potential threats can be proactively addressed, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to CUI.
NIST 800-171 System and Information Integrity Control Family
Ensuring the integrity of systems and information is crucial. Organizations must establish mechanisms to detect and prevent unauthorized changes to information, such as implementing file integrity monitoring systems and maintaining up-to-date antivirus software.
NIST 800-171 Incident Response Control Family
Having an effective incident response plan in place enables organizations to swiftly address security incidents and mitigate their impact. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing emergency communication channels, and regularly testing the incident response plan.
NIST 800-171 Access Control Family
Access controls play a vital role in protecting CUI. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, role-based access controls, and regular user access reviews are essential for preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
NIST 800-171 Risk Assessment Control Family
Regular risk assessments help organizations identify and prioritize potential risks associated with CUI. By evaluating threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts, organizations can implement appropriate security controls and measures.
NIST 800-171 Personnel Security Control Family
Organizations must establish personnel security policies and procedures to ensure that individuals with access to CUI are trustworthy and adequately trained. Conducting background checks, providing user awareness training , and enforcing disciplinary measures are crucial aspects of personnel security.
NIST 800-171 Configuration Management Control Family
Maintaining secure configurations for information systems is vital to protect CUI. Organizations must establish configuration management processes to ensure that systems are properly configured, patched, and updated to prevent potential security vulnerabilities.
NIST 800-171 Media Protection Control Family
Protecting physical and digital media that contain CUI and other sensitive content is critical. This includes implementing controls for proper handling, storage, transportation, and destruction of media to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure.
NIST 800-171 Physical Protection Control Family
Physical security measures are equally important in safeguarding CUI. Organizations must establish controls to restrict (but still monitor) physical access to sensitive areas, employ surveillance systems, and protect hardware and equipment from theft or damage.
Best Practices for Sharing CUI in Compliance With NIST 800-171
While the checklist is just an overview of the NIST 800-171 requirements, you should have by now a good indication of what your organization must do to adhere to this comprehensive security standard. Let’s now turn our attention to some best practices to accelerate your organization’s adherence to NIST 800-171, particularly as it applies to protecting CUI whenever you send it, receive it, share it, or store it.
Use Secure Protocols in All Communication Channels
Ensure that all communication channels, such as email, web forms, and file transfers, utilize secure protocols such as HTTPS, SFTP, or SSH. These protocols encrypt data transmission and protect CUI and other sensitive content against interception or tampering.
Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest
Implement end-to-end encryption to protect CUI from the instant it leaves the sender to the instant it hits the recipient’s inbox. This ensures that even if intercepted as it crosses the network firewall, the content remains unreadable. Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols should be used for securing network connections.
Secure Email Communications to Protect Sensitive Content
Secure email communications involves implementing measures to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of email messages and their attachments. Email is a widely used communication method, but it is susceptible to security risks such as interception, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Enforce the use of strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), for accessing communication systems, especially if an employee has to access the system remotely. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional proof of identity beyond just a username and password. By requiring users to provide multiple credentials, such as a password and a unique verification code, the risk of unauthorized access is significantly reduced.
Integrate Secure File Sharing and Secure File Transfer Systems With Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
Implement DLP solutions to monitor outgoing communications and prevent the unauthorized transmission of sensitive information. DLP solutions can detect CUI and other sensitive content and block it from leaving the organization, preventing malicious data leaks like intellectual property theft, or accidental leaks like misdelivery.
Update and Patch Software Regularly
Keep all systems and applications, including operating systems, web browsers, email clients, software, and firewalls, up to date with the latest versions. Apply security patches in a timely manner. Regular updates help address vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of exploitation.
Isolate Communications Network to Limit a Cyberattack’s Impact
Implement network segmentation to isolate sensitive communication systems and data from the rest of the network. This minimizes the potential impact of a security breach and prevents unauthorized access to critical resources outside of the communications network.
Conduct Regular Security Awareness Trainings
Educate employees about secure communication practices and good cyber hygiene, emphasizing the importance of data protection, phishing prevention, strong passwords, and recognizing phishing and other social engineering attacks. Regular training sessions help create a security-conscious culture within your organization.
Monitor and Audit Systems and Applications to Detect Anomalies
Implement robust monitoring and auditing mechanisms to detect and investigate security incidents early and effectively. By analyzing system logs, conducting regular audits, and implementing intrusion detection systems, organizations can identify and respond to potential threats promptly to mitigate the damage cybersecurity threats can pose.
This table summarizes the best practices for sharing CUI in compliance with NIST 800-171:
| Best Practice | Actionable Step |
|---|---|
| Use Secure Protocols in All Communication Channels | Ensure HTTPS, SFTP, or SSH protocols are used for email, web forms, and file transfers. |
| Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest | Implement end-to-end encryption with TLS or SSL protocols to protect content during transmission. |
| Secure Email Communications to Protect Sensitive Content | Implement measures to safeguard email confidentiality, integrity, and availability. |
| Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms | Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote access and use of strong authentication methods. |
| Integrate Secure File Sharing and Transfer Systems With DLP | Deploy DLP solutions to monitor and prevent unauthorized transmission of sensitive information. |
| Update and Patch Software Regularly | Keep systems and applications up to date, apply security patches, and maintain software currency. |
| Isolate Communications Network to Limit Cyberattack’s Impact | Implement network segmentation to isolate sensitive communication systems from the rest of the network. |
| Conduct Regular Security Awareness Trainings | Educate employees on secure communication practices, data protection, and recognizing social engineering attacks. |
| Monitor and Audit Systems and Applications to Detect Anomalies | Employ robust monitoring, auditing, and intrusion detection systems to identify and respond to threats. |
By following these best practices, organizations can strengthen their adherence to NIST 800-171 and enhance the security of CUI.
Use NIST 800-171 to Accelerate Compliance With Other Industry Regulations and Standards
While NIST 800-171 is specific to CUI protection, it influences other industry standards in terms of cybersecurity and data protection. Here are a few examples of how NIST 800-171 compliance can align with other standards:
NIST 800-171 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
Aligning NIST 800-171 with the NIST CSF can provide organizations with a comprehensive approach to enhancing their cybersecurity posture. The NIST CSF is a voluntary framework that offers a risk-based approach to managing and improving cybersecurity. By aligning NIST 800-171 with the NIST CSF, organizations can benefit from a holistic approach to cybersecurity. NIST 800-171 provides specific guidance for protecting sensitive information, while the NIST CSF offers a broader framework for managing cybersecurity risks. This alignment enables organizations to leverage the strengths of both frameworks, resulting in a comprehensive and risk-based approach to cybersecurity management.
NIST 800-171 and CMMC
NIST 800-171 and Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) are two frameworks developed to enhance the cybersecurity posture of organizations, particularly those working with the United States Department of Defense (DoD). While NIST 800-171 provides guidelines for protecting sensitive federal information in non-federal systems, CMMC establishes a unified cybersecurity standard for defense contractors and subcontractors. CMMC incorporates and expands upon NIST 800-171. CMMC compliance is crucial for organizations working with the DoD to ensure the security of CUI and other sensitive information.
NIST 800-171 and DFARS
While NIST 800-171 provides a set of security controls specifically designed to protect CUI in non-federal systems, DFARS, on the other hand, is a regulation enforced by the Department of Defense (DoD) that supplements the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR). It requires contractors and subcontractors that handle or process CUI to implement specific security measures outlined in NIST 800-171.
In essence, DFARS incorporates the security requirements of NIST 800-171 into contractual obligations for organizations working with the DoD. This means that organizations must comply with NIST 800-171 controls as a condition for doing business with the DoD.
The implementation of NIST 800-171 and compliance with DFARS are crucial for organizations seeking to participate in defense contracts or subcontracting opportunities. Adhering to these frameworks helps to ensure the protection of CUI and strengthens the overall cybersecurity posture of the defense supply chain.
NIST 800-171 and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Standards
ISO has developed a set of standards that address various aspects of information security, including ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System) and ISO 27002 (Code of Practice for Information Security Controls).
ISO standards provide a globally recognized framework for information security management. ISO certifications have many benefits, including enhanced credibility, international compliance, and harmonized security practices.
It’s worth noting that NIST 800-171 and ISO standards share some similarities in terms of their approach to security controls and risk management. Both frameworks emphasize the importance of implementing appropriate safeguards, conducting risk assessments, and continuously monitoring and improving security practices.
Adhering to NIST 800-171 can help and accelerate ISO 27001 certification and other related certifications by providing a solid foundation and alignment with internationally recognized best practices for information security. Here are some benefits of NIST 800-171 adherence in relation to ISO 27001 and similar certifications:
- Common Security Controls: NIST 800-171 includes a comprehensive set of security controls specifically tailored to protect controlled unclassified information (CUI). Many of these controls align with the requirements of ISO 27001 and other frameworks. By implementing NIST 800-171 controls, organizations can establish a strong foundation that aligns with the core security requirements of ISO 27001.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Both NIST 800-171 and ISO 27001 emphasize the importance of conducting risk assessments to identify and prioritize information security risks. Adhering to NIST 800-171 can contribute to the risk management processes required by ISO 27001, helping organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks to CUI effectively.
- Compliance Confidence: NIST 800-171 adherence demonstrates a commitment to meeting specific security requirements mandated by the U.S. government, particularly for organizations involved in the defense supply chain. This can provide a strong foundation and evidence of compliance when pursuing ISO 27001 certification, which is recognized globally as a robust information security management system.
- Documentation and Policies: NIST 800-171 compliance often involves the development of documentation and policies to support the implementation of security controls. These artifacts, such as system security plans, incident response plans, and access control policies, can be leveraged when seeking ISO 27001 certification, as they align with the documentation and policy requirements of ISO 27001.
- Continuous Improvement: Both NIST 800-171 and ISO 27001 emphasize the importance of continuous improvement in managing information security. By implementing NIST 800-171 controls, organizations establish a strong baseline and ongoing monitoring practices that align with the continuous improvement requirements of ISO 27001. This helps organizations maintain and enhance their security posture over time.
By aligning with NIST 800-171 and leveraging its security controls, organizations can streamline the process of achieving ISO 27001 certification. This alignment enhances the overall maturity and effectiveness of their information security management system and provides confidence to stakeholders that appropriate measures are in place to protect sensitive information. Additionally, ISO 27001 certification can provide broader recognition and credibility, expanding business opportunities beyond the scope of NIST 800-171 compliance.
NIST 800-171 and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation in the European Union that governs the protection of personal data and privacy rights of EU citizens and residents. While NIST 800-171 focuses on CUI protection, there are overlaps between the requirements of GDPR and NIST 800-171. For instance, both emphasize the need for appropriate security controls, risk assessments, incident response, and ongoing monitoring to protect sensitive data.
NIST 800-171 and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to protect payment card data and ensure the secure handling of cardholder information. NIST 800-171 can complement PCI DSS requirements by addressing broader information security aspects beyond payment card data. Implementing NIST 800-171 controls can contribute to an organization’s overall security posture and help meet certain PCI DSS requirements.
Security Controls Alignment: NIST 800-171 encompasses a comprehensive set of security controls that focus on protecting controlled unclassified information (CUI). Many of these controls overlap with the requirements of PCI DSS, such as access control, encryption, monitoring, and incident response. By implementing NIST 800-171 controls, organizations can establish a strong security baseline that aligns with several PCI DSS requirements.
Documentation and Policies: NIST 800-171 compliance typically involves developing documentation and policies to support the implementation of security controls. These artifacts, such as system security plans, incident response plans, and access control policies, can provide a strong foundation when creating documentation required by PCI DSS, such as security policies, procedures, and network diagrams. Leveraging the existing documentation can save time and effort during the PCI DSS compliance process.
Overall Security Maturity: Implementing NIST 800-171 controls contributes to an organization’s overall security maturity and readiness. While it may not cover all specific PCI DSS requirements, it establishes a strong foundation for addressing common security controls. By achieving compliance with NIST 800-171, organizations are better positioned to tackle the remaining PCI DSS requirements and demonstrate a robust security posture.
It’s important to note that achieving NIST 800-171 compliance does not automatically guarantee PCI DSS compliance. PCI DSS has its own specific requirements that organizations must address, such as cardholder data storage, network segmentation, and payment application security. However, NIST 800-171 can provide a valuable starting point and support in meeting several security controls and risk management aspects of PCI DSS. Organizations should carefully assess and address all relevant PCI DSS requirements to ensure full compliance.
Kiteworks Helps Organizations Comply With NIST 800-171
Adherence to NIST 800-171 is essential for organizations seeking to work with the federal government. Compliance with this framework demonstrates a commitment to protecting CUI, which is crucial when handling sensitive government data. However, the benefits of NIST 800-171 adherence extend beyond government contracts.
By implementing NIST 800-171 controls, organizations can gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. They showcase their commitment to data protection, giving potential customers and partners confidence in their security practices. This can lead to increased trust, improved business relationships, and enhanced opportunities for collaboration.
Moreover, aligning with NIST 800-171 can also accelerate compliance with other regulations and standards. The framework covers a wide range of security controls that align with industry best practices.
Here’s how Kiteworks helps organizations adhere to NIST 800-171 so they can work with the federal government AND accelerate compliance with other regulations and standards.
- Private Content Network: The Kiteworks Private Content Network unifies, secures, controls, and tracks the CUI and other sensitive content that public and private sector organizations share within and outside their organizations. This not only ensures NIST 800-171 compliance but also compliance with other regulations like GDPR, FedRAMP, and CMMC. It is a FedRAMP authorized solution for Moderate level CUI that encrypts data in transit and at rest with TLS 1.2 and AES-256 encryption, respectively.
- Hardened Virtual Appliance: The Kiteworks hardened virtual appliance is a secure communications platform designed for government agencies and other organizations with stringent security requirements. This appliance provides a highly secure environment for sharing sensitive information, such as classified data, policy documents, or legal materials. It offers robust security features to demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations. The hardened virtual appliance can be deployed on-premises or in a private cloud, providing flexibility and control over the organization’s data storage and security infrastructure.
- Secure File Sharing: Kiteworks provides a secure platform for sharing files and documents both internally and externally. It employs encryption and secure protocols to protect data during transit and at rest, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of CUI.
- Access Controls: Kiteworks allows administrators to define granular access controls, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access CUI. Role-based permissions can be implemented to restrict access to sensitive information, aligning with the access control requirements of NIST 800-171.
- Data Loss Prevention: Kiteworks DLP integration capabilities prevent the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data. It can detect and block the sharing of files that contain CUI or other predefined sensitive information, reducing the risk of accidental or intentional data leaks.
To learn more about Kiteworks and how the Private Content Network helps organizations achieve NIST 800-171 compliance, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Blog Post NIST 800-171 Compliant File Sharing – What You Need to Know and How Kiteworks Can Help
- Article Protecting CUI With NIST SP 800-171: How to Stay Compliant
- Blog Post What Is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)?
- Blog Post Protecting Business With the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- Blog Post NIST Privacy Framework for Protecting Sensitive Data